SSH Config File Location sshd conf file settings ssh server ubuntu
The SSH config file location and settings for an SSH server on Ubuntu involve several key aspects. The main OpenSSH server settings are stored in the configuration file sshd_config, which is located at /etc/ssh/sshd_config. Before making any changes, it is recommended to create a backup of this file using the command sudo cp /etc/ssh/sshd_config /etc/ssh/sshd_config.initial
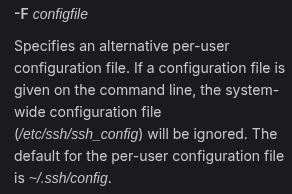
For client-side configurations, the SSH config file is typically located in the ~/.ssh/config directory for user-specific settings. This file allows users to define various parameters to simplify and automate SSH connections. For example, you can specify the hostname, username, and identity file for a particular server.
In addition to the main configuration file, there are other settings and parameters that can be configured to enhance security and functionality. These include changing the default port to a more secure one within the dynamic range (49152 - 65535), enabling key-based authentication instead of password authentication, and configuring various other options such as address family, batch mode, and compression.
If you need to create the SSH config file, you can do so by creating the ~/.ssh directory if it does not exist and then using a text editor to create and edit the config file within it. The file requires strict permissions, typically set to 0600 for the user.
For system-wide configurations, the file is located at /etc/ssh/ssh_config This file can be used to set default values for all users on the system.
In summary, the SSH config file location for the server is /etc/ssh/sshd_config and for client-side configurations, it is ~/.ssh/config These files allow for detailed configuration of SSH connections to enhance security and convenience.
reload ssh
To apply changes made to the SSH configuration files on an Ubuntu system, you need to reload the SSH service. This can be done using the following command:
sudo systemctl reload sshAlternatively, you can also use:
sudo service ssh reloadThese commands will reload the SSH daemon, applying any changes made to the configuration files without requiring a full system reboot. It is important to ensure that the syntax of the configuration file is correct before reloading to avoid any issues with the SSH service. If there is an error in the configuration file, the reload command will fail, and you will need to correct the error before attempting to reload again.
Leo AI generated answer. Please verify critical facts.